In Binary Tree the Inorder successor is the next node in Inorder traversal. The inorder successor of the root is the leftmost element in the right subtree. In the Binary Search tree, the Inorder successor of an input node can be defined as the node with the smallest value greater than the value of the input node. Basically, you can say that the next node in the sorted node will be the Inorder successor of the previous node.
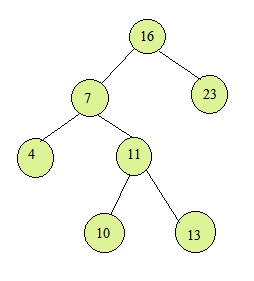
In this BST the inorder successor of 10 is 11 and 13 is 16. As you can see that it is the next node in the sorted order nodes.
Algorithm :
1) The first step is to check whether there is a right subtree of the input node or not. If there is a right subtree then find the minimum value node in that and return that will be the inorder successor of the input node.
2) If there is not then move upwards and start from the root and follow the search technique if the value of the input node is less than the root node then move towards left otherwise right and return successor.
Program :
/*I will be writing only the functions rather than the whole program*/
struct node
{
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
}
struct node* minvalue(node)
{
node* current_node=node;
while(current_node->left!=NULL)
{
current_node=current_node->left
}
return current_node;
}
struct node* inordersuccessor(node* root,node* inputnode)
{
if(inputnode->right!=NULL)
return minvalue(inputnode->right);
struct node* successor=NULL;
while(root!=NULL)
{
if(inputnode->data<root->data)
{
successor=root;
root=root->left;
}
else if (inputnode->data>root->data)
{
root=root->right;
}
}
return successor;
}
In this BST the inorder successor of 10 is 11 and 13 is 16. As you can see that it is the next node in the sorted order nodes.
Algorithm :
1) The first step is to check whether there is a right subtree of the input node or not. If there is a right subtree then find the minimum value node in that and return that will be the inorder successor of the input node.
2) If there is not then move upwards and start from the root and follow the search technique if the value of the input node is less than the root node then move towards left otherwise right and return successor.
Program :
/*I will be writing only the functions rather than the whole program*/
struct node
{
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
}
struct node* minvalue(node)
{
node* current_node=node;
while(current_node->left!=NULL)
{
current_node=current_node->left
}
return current_node;
}
struct node* inordersuccessor(node* root,node* inputnode)
{
if(inputnode->right!=NULL)
return minvalue(inputnode->right);
struct node* successor=NULL;
while(root!=NULL)
{
if(inputnode->data<root->data)
{
successor=root;
root=root->left;
}
else if (inputnode->data>root->data)
{
root=root->right;
}
}
return successor;
}
Comments
Post a Comment