[ Updated for 2026] :
[This article was originally written in 2022 and has been revised to reflect current Data Engineering trends.]
Why SQL Still Matters for Data Engineers in 2026
Despite the rise of modern data stacks, cloud platforms, SQL remains one of the most critical skills for Data Engineers. In fact, SQL is often the first technical filter in Data Engineering interviews across startups, product companies, and large enterprises. Generally, there is a perception that SQL interviews are only for Data Analysts or Business Analysts but that's not the case. Writing SQL are essential part of Data Engineering specially for ELT pipelines that involves dbt.
In 2026, SQL interviews are no longer about memorizing syntax. Interviewers focus on:
-
How you think in SQL
-
How you model and transform data
-
How you handle scale, performance, and correctness
- How SQL supports analytics, reporting, and AI pipeline
In this post, we are going to provide the frequently asked SQL interview questions and asked in Data Engineer Interviews. Interviewers usually go from asking fundamental SQL interview queries to asking advanced SQL queries. We will cover both in this post.A. Basic SQL Questions
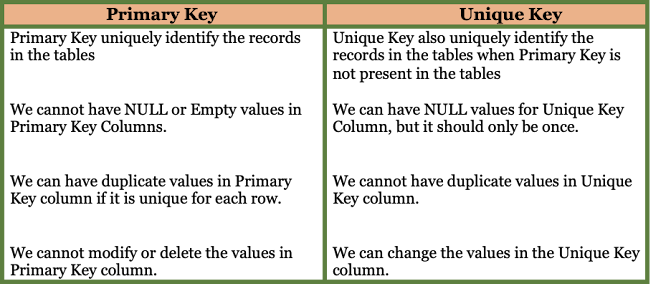
1. What is a Primary Key?
A Primary key is a field or combination of fields that uniquely identify the records in the tables. The primary key column cannot be NULL or Empty. The primary key column should be unique and the table cannot contain more than one Primary Key.
For Example, the Employees in the company can be uniquely identified by the employee_id, so employee_id is Primary Key for the Employee table in the Company database. We can define a Primary Key using the below syntax.
CREATE TABLE Employee (
employee_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(45),
);
2. What is a Unique Key?
A Unique Key in SQL is a field or the combination of fields that ensure all the values in the columns are unique i.e. column cannot contain duplicate values. Unlike, Primary Key Unique Key allows to store NULL value in the column but only one NULL value per column.
For Example, an email for each employee in the company should be Unique. We can define a Unique Key using the below syntax.
CREATE TABLE Employee (
email UNIQUE,
name VARCHAR(45),
);
3. What is the difference between a Primary Key and Unique Key?
4. What is Normalization in the DBMS?
Normalization is the process of structuring a table in DBMS such that it reduces redundancy and dependencies, inconsistencies and anomalies in the Database. There are different levels of Normalization listed below
- First Normal Form (1NF)
- Second Normal Form (2NF)
- Third Normal Form (3NF)
- Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF)
5. Explain each of the Normal Forms briefly.
6. What is an index in SQL?
Indexes are lookup tables that help in the faster retrieval of records from the table. Basically, an index is a pointer to the table that increases records retrieval performance by directly accessing the required records.
Let's look at a simple example, when you want to read a specific chapter or a topic in a book, you look up in the index and directly retrieve the chapter using the page number. An index can be a single column or a group of columns.
We can define an index of the single column using the below syntax.
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table_name (column_name);
7. What is Clustered index in SQL?
A clustered index defines the order of data that is physically stored in the table. There can be only one clustered index in the table and it stores the data in the sorted form.
For example, if the employee_id is clustered index in the Employee table, then it will store all the employee_ids in the sorted order and if you want to insert new employee_id 5 then it will insert the employee_id in the 5th row rather than inserting it at the top of the table.
In SQL, Primary Key constraints automatically create a Clustered index for the Primary Key column.
8. What is a Non-Clustered index in SQL?
A Non-Clustered index doesn't define the order of the data that is physically stored in the table, instead, it only maintains the logical order of the data as the non-clustered index is stored separately from the data.
This allows having more than one Non-clustered index in a table. The main purpose of creating a Non-Clustered index is to search the data.
Let's look at the example to understand this. In Books, we have book content in one place and all the index at another place, usually at the start of the book.
9. What is the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE in SQL?
10. What is TRIGGER in SQL?
TRIGGER is a stored procedure that is automatically called or invoked whenever a certain event occurs in DBMS. These events are usually DML statements given to the system.
Using TRIGGER we can execute a block of code when an insert, update or delete statements are executed against a table.
TRIGGER has two main components, the first is action and the other is an event. When actions are triggered certain events occur.
We can create a TRIGGER statement using the below syntax.
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
(AFTER | BEFORE) (INSERT | UPDATE | DELETE)
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
--variable declarations
--trigger code
END;
B. Advanced SQL questions complied list.
2. Confirmation-Rate: The confirmation rate of a user is the number of 'confirmed' messages divided by the total number of requested confirmation messages. The confirmation rate of a user that did not request any confirmation messages is 0.
3. Monthly Transactions: Need to write an SQL query to find for each month and country, the number of transactions and their total amount, the number of approved transactions and their total amount.
4. Food Delivery: Need to Write an SQL query to find the percentage of immediate orders in the first orders of all customers
5. Game Play Analysis: Need to write an SQL to report the fraction of players that logged in again on the day after the day they first logged in, rounded to 2 decimal places. In other words, you need to determine the number of players who logged in on the day immediately following their initial login, and divide it by the number of total players.
6. Consecutive Numbers: Need to Find all numbers that appear at least three times consecutively.
7. Last Person to fit in Bus: Need to write an SQL to find the person_name of the last person that can fit on the bus without exceeding the weight limit. The test cases are generated such that the first person does not exceed the weight limit.
8. Exchange Seats: Need to write a solution to swap the seat id of every two consecutive students. If the number of students is odd, the id of the last student is not swapped.


Comments
Post a Comment